SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is one of the most effective forms of online marketing, which involves arranging all aspects of a website to be more visible in the SERP results and thus receive more organic unpaid traffic.
In order to improve your rankings, you need to create an adequate plan tailored to your site’s needs. There are many SEO strategies, and it is not enough to pick one randomly and apply it. In addition, you must follow the latest updates of Google algorithms and adapt to new changes.
Trying to follow SEO innovations can be exhausting and lead to mistakes that can cause serious consequences – you can lose significant organic traffic or even get penalized by Google.
Sometimes, you are unaware of the common SEO mistakes you’re committing. You notice website rankings stagnate or decline, even though you’re doing SEO and expecting results.
Don’t worry – you’re in the right place. We’ve compiled a list of common SEO mistakes that even professionals make and ways to fix them.
On-page SEO mistakes
On-page optimization refers to actions you can take on your website that directly affect your SERP rankings.
Creating quality and authentic content is the foundation of on-page SEO, including keyword research, content planning, content structuring, image optimization, and numerous other tactics.
When creating an on-page strategy, mistakes can occur. Those mistakes negatively affect all important indicators of successfully implemented SEO. Below we identify them and find a way to fix them.
Outdated Website Content
Google is all about the user experience, and outdated content does not provide relevant information or match search intent. Users read old content, do not get an answer to their questions, feel frustrated, and go on a further search for information, which leads to a higher bounce rate. You will lose significant organic traffic because when filtering search results, Google will notice that your content is outdated and will not show it to users.
The solution:
Outdated content is one of the most common SEO mistakes. Focused on adding new articles, site administrators forget to audit old ones. You can edit some old articles and supplement them with fresh information; you can also change the years in the titles, while some posts will have to be archived.
You can use Google Search Console to update content.
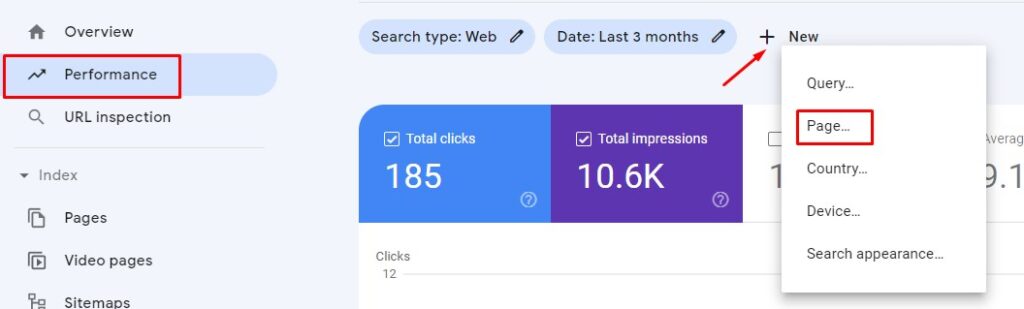
Open Google Search Console, go to “Performance,” and click on the “Pages” link next to “Queries.” In the “add property” box, enter the URL of the page you want to refresh with new information. When you open your page, click on the URL, and the report will show statistics.
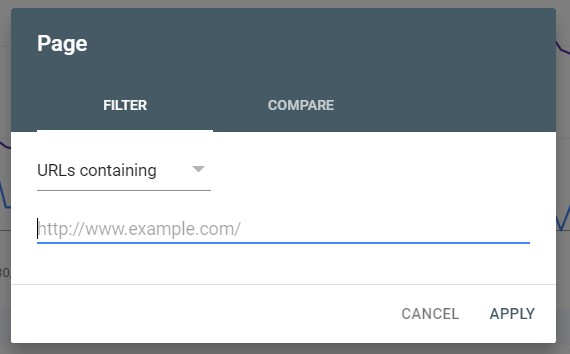
Click on “Queries,” and you’ll get a view of the keywords your page is currently ranking for. Google Search Console will show the phrases that got the most clicks first, but you can also sort by impressions. See which keywords and phrases are currently generating the most organic traffic. Compare those words to the words within the following elements of your page: Title Tag, H1, H2, Body Content, and Alt Tags. You can also use those keywords for interlinking from other pages that are relevant
If some words are not included in these elements of your website, find a way to incorporate them in your content. Your ranking for those phrases will lead to increased traffic.
Ensure you always provide quality, fresh and relevant information to your readers. They’ll appreciate it – and Google will, too.
Targeting wrong keywords
Keyword research is one of the foundations of on-page SEO optimization. There are many types of keywords in SEO, and one can easily make a mistake in this field. If you target keywords incorrectly, you will build a house without a foundation – therefore, unsuccessfully. This applies to overly general (short-tail keywords with high search volume) and keywords that are not relevant to your industry. This common SEO mistake will result in poor rankings, low organic traffic, and insufficient conversion.
The solution:
Research, research, and more research. Once you’ve discovered all the keywords you’d like to rank for, it’s time for a reality check – what are realistic options for your online presence and domain authority?
Don’t waste your time trying to rank for short-tail keywords if you have a new website. Even well-known brands can find it challenging to rank in one of the top 10 spots for words like “book,” “perfume,” or “mobile phone.” Keep your focus on long-tail keywords. You can research long-tail keywords using the Ahrefs tool. Remember that people with transactional search intent browse such keywords, resulting in higher conversions.
Once you’ve created your keyword plan, divide them into clusters: one general topic that branches into more specific ones that answer readers’ questions and solve problems.
Lack of internal linking
Internal links are vital for SEO because they tell Google about the content and relevance of your pages, allowing them to rank higher. Interlinks with carefully selected anchor text tell Google about the linked pages’ content and hierarchy.
You can also think of interlinks as signposts showing where visitors can learn more about a topic. Missing internal links is a frequent SEO mistake that you should fix ASAP.
The solution:
You’ll solve the lack of an interlinking strategy by simply linking related content, but be cautious and attentive. You can’t link pages because they look similar to you. Follow these rules:
- Use descriptive anchor texts instead of linking just one word. This rule is important for the accessibility of your site.
- Most sites have an internal link to a “contact us” page, which is often unnecessary, although it is considered a call to action. Interlink meaningful content deep within the site rather than pages in major categories that readers can easily find.
- Add interlinks only to relevant pages that the visitor could gain additional value by reading. Do not interlink pages whose content is unrelated.
- Use interlinks sparingly. No one knows the exact number of “allowed” interlinks per page, but use common sense and don’t overdo it.
Keyword cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization is another SEO mistake that many experienced specialists and SEO content writers make. Keyword cannibalization is a term we use to describe the use of identical or similar keywords and phrases on different pages of a site. As a result, instead of competing with your competition, your site’s pages compete with each other. Google often does not know how to rank them and prioritizes a page you did not favor or worse – don’t rank either of them.
The solution:
To correct keyword cannibalization, you must first identify it. You can do this with keyword research tools like Ahrefs. Enter your site’s URL in the Site Explorer section, then look at Organic keywords (menu on the left), check the “Multiple URLs only” button, and you will see which keywords each ranks for.
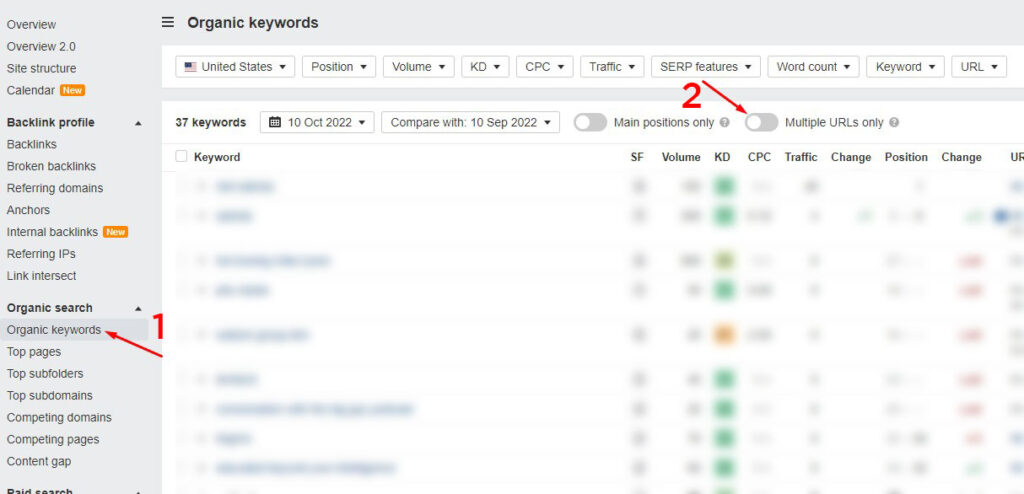
Once you identify pages competing with the same or similar keywords, fix them!
- Create new landing pages.
- Merge the content of pages with cannibalization problems into one page.
- Research new keywords that you could use in your SEO strategy.
- Use a 301 redirect to direct cannibalized content to another more authoritative page.
Poor or missing content structure
The poor content structure includes missing or misaligned headings, content crammed into thick walls of text, and similar errors. Such content is not easily navigated and readable by visitors, and Google never ranks it as high as it could be if it was properly structured.
The solution:
Choose wisely H1 title. The H1 must tell the reader and search engines the page’s content before they land on it. Have H2 tags for major content sections and H3 and H4 tags for sub-sections. The structure of your content should be categorized so well that the reader can deduce what the content is from the headlines alone, without actually reading the text.
The proper content structure will allow you to rank better and increase your chances of ending up in the featured snippets.
Publishing plagiarized content
Plagiarizing other people’s content is a big NO which Google strictly sanctions. When you copy content from someone else’s site and post it as your own, you’re not bringing any value – in fact, you’re causing harm because you’re disparaging someone else’s work. The penalties for plagiarized content are severe.
The solution:
This common SEO mistake is easy to avoid – just don’t copy other people’s content! Analyze the competition and find another approach to the topic you are writing about. Be innovative and original.
Google always recognizes plagiarized content and it never ranks it well. Creating original content takes a lot of time and effort, but it’s the only one that gets results. You’ll establish yourself as an authority in your industry, which readers and search engines will appreciate.
What about general information that just isn’t original? Some things are facts, and there is not a lot of improvisation, but try to approach the presentation of this content innovatively: add images, tables, lists, infographics – content that could be interesting to your audience.
Tip: To check whether your text is plagiarized by someone else, you can use the following tools:
Technical SEO mistakes
While on-page SEO is directly responsible for attracting organic traffic, technical SEO ensures that search engines better understand the overall picture of the entire site, as well as that the site provides a better user experience. Without technical SEO, your rankings would sink, and there would be no way to get them back up. That is why it’s important to be aware of common technical SEO mistakes and how you can fix them.
Broken images and missing alternative texts
Alternative text, or, more simply, alt text, is an HTML attribute that tells about the image’s content. Alt text increases the accessibility of your site for people with visual impairments who access the Internet using screen readers. Also, Google can’t see pictures on your site, so it needs alt text to tell it what the image shows.
Alt text is important for SEO for the reasons just mentioned, but if it is reinforced with keywords, it further contributes to the website’s ranking.
Missing alt text and broken images, often caused by an incorrect file name or wrong extension, are common SEO mistakes.
The solution:
Fixing this SEO error is simple: simply fill in all missing alt tags retroactively and enter them in the future as soon as you add an image to the site.
First, ensure the image exists on the site to solve the broken image problem. If it is not there, simply upload a new one and add the required alt and title tag. If the image exists and is still broken, make sure the image names match. Even minor differences, such as dash and underscore, can create a problem in the image display. Note the errors in the code – “midnight-sky.jpg” versus “midnight _sky.jpg”.
Broken or redirected links
Broken links are highly harmful to your SEO because they decrease conversion and increase bounce rates, creating a poor user experience. Also, Google may stop indexing and crawling your site if it encounters multiple broken links, which results in some important pages of your site being unindexed.
The solution:
Use the “crawl stats” function of the Google Search Console to identify pages with broken links. You can also find them using Ahrefs by following these steps:
- Open Site Explorer
- Enter name of your domain (full url)
- Go to section “Pages”
- Click on Best by Links
- From HTTP code dropdown menu choose “404 not found”
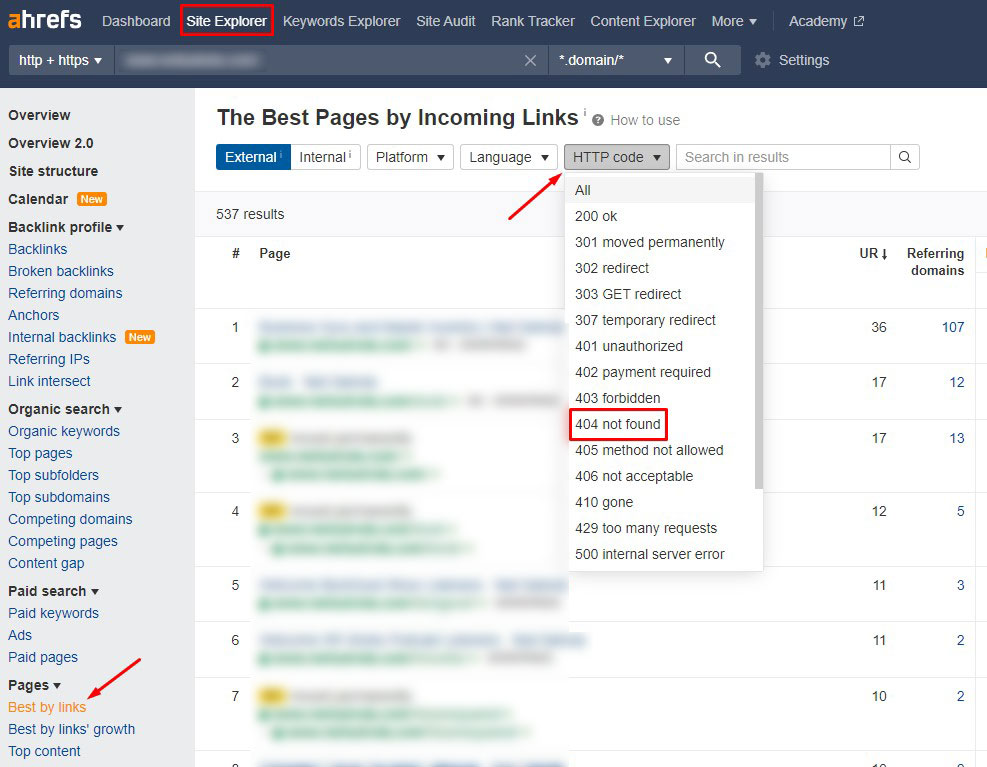
You will fix internal links by quickly replacing or creating new content on a given page or by using a 301 redirect to direct your audience to other, similar content on your page.
To repair broken external links, contact the administrator of the site from which the link comes or if the domain is no longer active, simply remove the link.
Not indexed pages
For Google to display your pages in the SERP, they must first be indexed; otherwise, they will be invisible. Reasons why your pages are not indexed can be:
- 404 errors
- Noindex and nofollow meta tags
- Duplicate content
- Low domain authority
- Page is not on the sitemap
The solution:
You can request indexing of your pages in Google Search Console. Select properties and enter the URL of your site so that Google will crawl it. Click on the “Request Indexing” option and regularly check the status of your URL on the “Inspection Tool.”
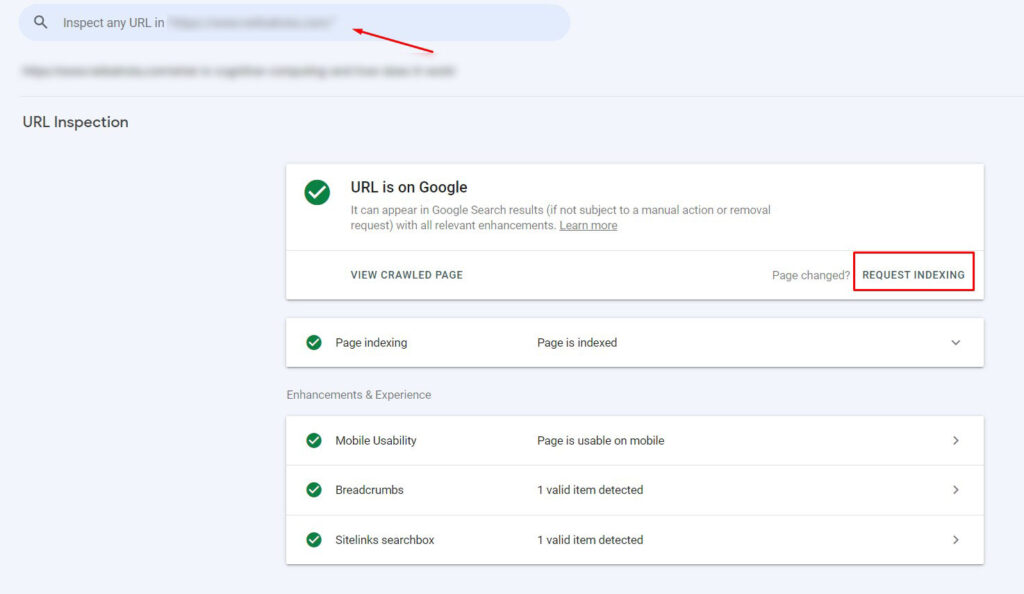
A sitemap tells Google about the hierarchy of the pages on your site, which also impacts indexing. To check if a page is not indexed on the sitemap, use the URL checker tool in Google Search Console. If you get a result of “URL not in Google” and “Sitemap: N/A,” the page is not in your sitemap nor indexed.
Sitemap problems
A sitemap explains to search engines the hierarchy of your site’s pages, allowing them to crawl and index them. Also, it helps to simplify the site’s content and simplify navigation. If the sitemap is missing or has errors, the site’s pages may remain unindexed, and the structure of your site may be unclear.
The solution:
If you don’t have a sitemap, create it and submit it. You will soon see its importance for SEO – search engines will send spiders to crawl your pages and index them, and you will appear in the search results.
However, a sitemap with errors is just as bad (if not more damaging) than a missing sitemap. Be careful not to make the following mistakes when creating your sitemap:
- Do not list pages marked with “noindex.”
- Make sure you don’t forget to add important pages. Pages you do not specify will not be indexed.
- You don’t submit a sitemap to Google when you create it, and it remains unaware of its existence.
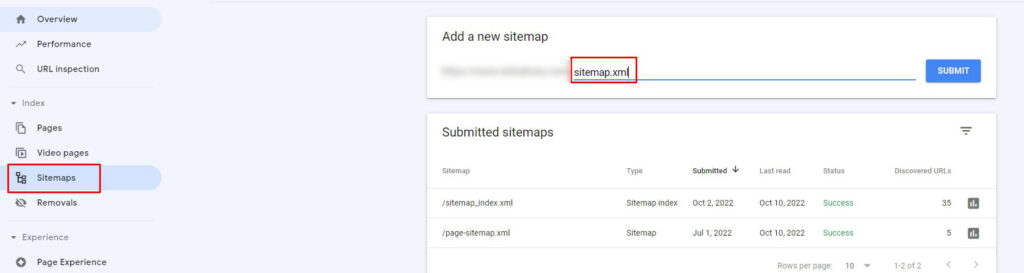
Tip: To submit your sitemap to Google, follow these steps:
- Go to Google Search Console.
- In the sidebar, type your site’s URL.
- Click on the “Sitemaps” menu under the “Index” section.
- Remove old sitemap (if it exists).
- Enter link to your sitemap in the “Add a new sitemap” field.
- Submit.
Long URLs
A URL is the address of a web page, and its length impacts SEO. The URL should have a maximum size of 2083 characters or 512 pixels so that Google does not shorten it when displaying it and can be accessed correctly in all browsers.
The URL appears garbled when using too many stoppers and spaces, HTTP connection instead of HTTPS, and using more than two folders in the URL, resulting in a poor user experience.
The solution:
A proper URL length and readability are important to search engines and your audience.
Here’s how to solve the messy URL problem:
- Always create short and readable URLs because the audience tends to click on them more often. A neat URL looks better and gets shared more often.
- Shorter URLs rank better than longer ones.
- Do not use capital letters in the URL.
- Use keywords in the URL and separate them with dashes instead of underscores.
- Always use an HTTPS connection (make sure you have an SSL certificate). As we mentioned, user experience is significant to Google, and a secure connection that prevents data theft and misuse is the basis of a good user experience.
Need help fixing the most common SEO mistakes?
SEO information and best practices emerge almost every day. Sometimes it can be challenging to keep up with all the innovations, so mistakes are inevitable – they can happen even to the most experienced SEO specialists.
When common SEO errors occur, the indicator will be a slowdown in traffic or conversions, so you must know how to identify and fix them.
Don’t hesitate to contact us if you’re making common SEO mistakes and need help resolving them. Long-term experience creating personalized SEO strategies has positioned LeadIn Media’s SEO specialists as leaders in optimization. We will ensure that your site works flawlessly and quickly finds its way to the top of SERP.




